DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization),” a term which has been attracting a great deal of attention along with “Web 3.0” and “NFT” since 2022, has become a hot topic as a new form of organization different from existing organizational structures. In this issue, we will introduce an overview of DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations), their structure, and examples of their use in Japan and overseas.
What is a DAO? What makes it different from previous organizations?
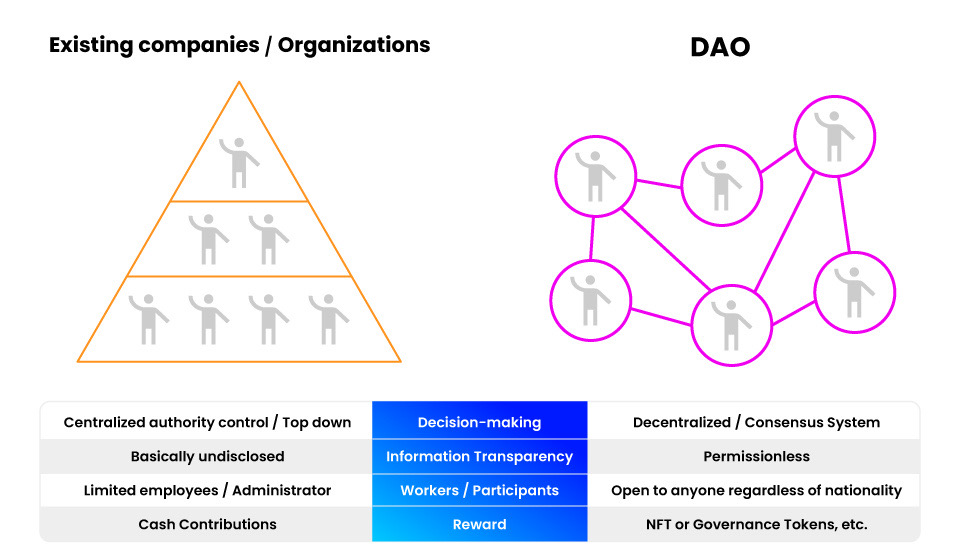
DAOs, called decentralized autonomous organizations in Japanese, are one of the new organizational structure systems that have become mainstream topics since 2022. The main characteristics of DAOs are that there is no central administrator, and each participant is allowed to participate regardless of nationality or gender, and is given fair discretionary rights.
The details of how DAOs work will be introduced later, but the key emphasis is that all the organization’s operations are recorded by smart contracts within the system and can be completed over the Internet. The main reason why DAOs are attracting attention now is that they can realize a more democratic management system, since decisions on management policies are made by voting using the governance tokens given to each participant.
In addition, the basic concept of DAO is the same as the values of Web 3.0: to activate person-to-person transactions through P2P via a decentralized network based on blockchain technology, and to return the sovereignty of information to the hands of individuals to create a democratic, decentralized and controlled-environment organization.
For more information on Web 3.0, please see the following column. >>
https://ctia.ltd/en/column_20220617en/
<Characteristics>
- No central administrator
- Each participant is given fair discretion
- Participation is open to all regardless of nationality or gender
In a stock company with a traditional corporate or organizational structure, the president/CEO, the decision maker, receives capital from shareholders in exchange for shares issued, and top-down decisions are made on hiring executives and employees and on the use of operating funds for the business, based on the corporate policy and philosophy. Basically, this decision-making is done privately away from the outside world and is often not disclosed even to some employees and operators, which means that information transparency is often limited.
Not only in stock companies, but also administrative organizations such as municipalities headed by a chief executive (mayor or prefectural governor) and non-profit organizations such as NGOs represented by directors, etc., operate under a centralized organization, albeit in a different form. Compared to these existing organizational structures, DAOs have differing characteristics.
Decentralized Autonomy with Governance Tokens
There are three main characteristics that are important in introducing the DAO system.
No central administrator
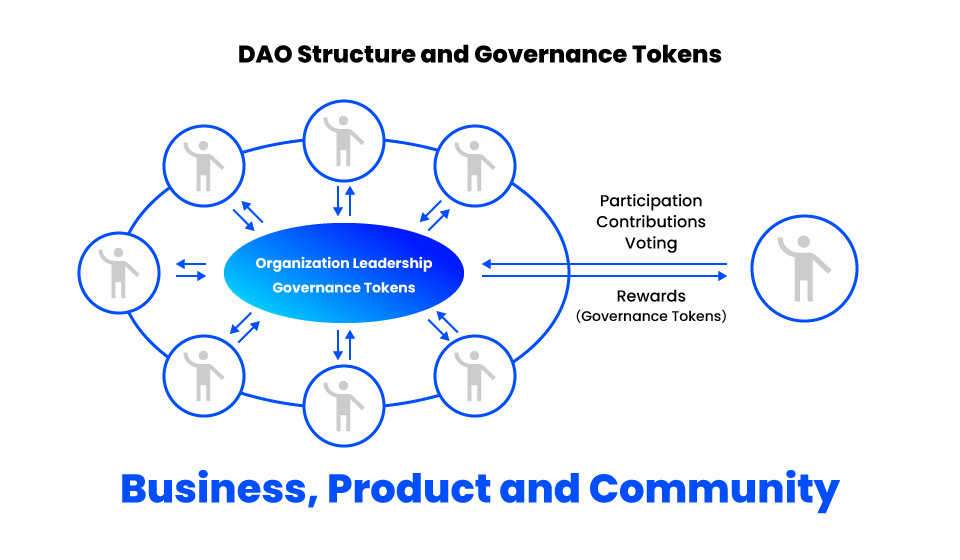
There is no central administrator, such as a decision-making leader, in a DAO. Instead, DAO participants are given the right to vote on operational policies as a governance token in exchange for their financial investment and project contributions.
These governance tokens record the history of operations, contributions, and decision-making results on the blockchain, and the information is automatically written by smart contracts. The main authority of the governance token is the management role in operation and the authority to change the program that is the basis of the project.
Collaborative and democratic organizational management
Decision-making in the DAO is done by a vote of each participant, like a committee. It is a consensus organization in which participants with tokens are free to make suggestions for improvements in the projects they participate in and vote on them, prioritizing them for improvement.
Since information related to operating policies recorded on the blockchain can also be referenced by anyone without the permission of the administrator, the possibility of fraud is low and information is highly transparent.
Rewards for participation contributions are tokens rather than cash
The amount of reward granted to DAO participants varies depending on the level of contribution and management policy, but the means of payment is exchanged in specific tokens rather than cash.
Participants receive consideration set by each project’s policy, such as a DAO that grants NFTs to participants or a portion of the transaction fee to the governance token holders for the long-term operation of the project.
As an analogy for the above characteristics of DAOs and their unprecedented organizational structure, it is said that “a DAO is a business, a product, and a community.” That participants who come together for a common purpose can form a unique community, and the opinions and policies they propose can add value and enhance brand power, is the reason why DAOs are described as being a business, a product itself, and a community.
Merits and Demerits of a DAO
There are three main benefits derived from the features of a DAO.
First, there is no central manager and participants have equal authority, making it easy for anyone to freely offer opinions and suggestions on management policies. The centralization of authority has the potential to cause management to forcibly alter operations or improve work unreasonably, which can affect the reputation of the organization and the project.
One of the advantages of the DAO is the freedom to discuss opinions and suggestions on the operation by participants with fairly distributed authority, regardless of nationality or gender.
Second, because decision-making is open, it is difficult for fraud to occur and the transparency of the organization is high. Information and history related to operations are recorded on the blockchain, and accessible without permission from administrators, etc.
Participants can have access. Even if there is fraud by a participant, the cause can be easily discovered in an open environment. The fraud itself leads to a loss of trust in the community and the value of the business, so it is important to reduce credit risk.
Third, a sense of community is easily heightened: DAOs can assign positions to participants that match their abilities and skills, and participants can make decisions and vote within the scope of those positions. The fact that their opinions are respected and reflected in DAOs motivates the members to be involved, leading to an increased sense of belonging to the organization and a sense of accomplishment in the management of the organization.
<Merits>
- Easy for participants to share opinions and suggestions
- High organizational transparency due to open decision-making
- Easier to develop a sense of belonging
On the other hand, there are also risks and disadvantages associated with the organizational structure of DAOs.
First, DAOs, which conduct all transactions and operations over the Internet, are at risk of hacking. In 2016, the decentralized investment organization The DAO* made headlines for raising JPY 15 billion in operating funds, but a bug in the operating platform led to the theft of 5.2 billion yen worth of funds through a hack that exploited the vulnerability.
In that incident, the DAO took action to recover the assets by reverting the blockchain back to the way it was before the hack with the consent of the DAO participants. While the digital consistency of operations, transactions, and fund management is an advantage, caution should be exercised when participating and operating because of the risk of hacking.
On the other hand, there are also risks and disadvantages associated with the organizational structure of DAOs.
First, DAOs, which conduct all transactions and operations over the Internet, are at risk of hacking. In 2016, the decentralized investment organization The DAO* made headlines for raising JPY 15 billion in operating funds, but a bug in the operating platform led to the theft of 5.2 billion yen worth of funds through a hack that exploited the vulnerability.
In that incident, the DAO took action to recover the assets by reverting the blockchain back to the way it was before the hack with the consent of the DAO participants. While the digital consistency of operations, transactions, and fund management is an advantage, caution should be exercised when participating and operating because of the risk of hacking.
* The DAO … A project of a decentralized investment organization launched on the Ethereum platform. The investment destination is decided by the votes of the fund participants, and the profits are distributed to the investors as governance tokens.
Second, decision-making in organizational management may slow down.
In a pyramid-shaped, top-down organization, there are fewer decision makers, so its speed is faster. On the other hand, in a DAO, decisions are made by a vote of participants who hold governance tokens, so it takes time to make policy decisions. In the case of solving the hacking problem described above, where an immediate response was required, voting and decision-making could become a time-consuming and delaying factor.
Another drawback is the lack of legal framework, as DAOs are a new organizational structure and, like Web 3.0, crypto assets, and blockchain, the current global legal framework has not yet caught up. In many countries, dealing with hacking and legal issues is also a matter of self-responsibility, so news of the development of a legal framework in the future will be a point of focus.
<Demerits>
- Risk of hacking involved
- May slow down decision making in organizational management
- Legislation has not kept pace
Examples of DAO use to spark business creation and regional revitalization
As DAOs become a hot topic, examples of new project launches and regional revitalization utilizing DAOs are spreading both domestically and internationally. Here are some of them.
Ninja DAO
Ninja DAO, a popular NFT collection creation DAO from Japan, currently has about 40,000 participants. The main character Crypto Ninja is presented as an NFT collection, and participants can use the NFT creations to create secondary works.
Within Ninja DAO, there are many spin-off projects and new projects, such as music production by creators and game production with other companies. A high degree of creative freedom and an active community in a wide range of fields have been formed.
Yamakoshi Resident Association
Nagaoka City (formerly Yamakoshi Village) in Niigata Prefecture took measures to address population decline by selling NFT art of Nishiki-koi for the world’s first electronic resident registration card, and by welcoming the digital residents who purchased and owned the NFT as a community in the DAO, the “Yamakoshi Resident Association”. As a result, approximately 1,000 digital residents were created, more than the 800 real residents, and while discussing measures to revitalize the neighborhood within the DAO, the number of related residents and interactions outside the community have increased.
An increasing number of municipalities and rural areas in Japan that are considered marginalized communities are utilizing DAOs to secure independent financial resources and resolve human resource shortages, and they are attracting attention as a spark for regional revitalization.
Constitution DAO
n November 2021, the “Constitution DAO,” was launched as a way to bid on the original U.S. Constitution that was sold at auction in the U.S. Within the DAO, crowdfunding was conducted by participants who gathered to bid on the actual collection, and in just one week, $47 million (approximately JPY 5.4 billion at the time) was raised.
Although the resulting bid was not achieved due to a lack of funds required for the proper management of the original constitutional documents, it was one of the instances that led to the development of the DAO. Currently, this activity by the core members of the DAO has been terminated and all funds raised have been refunded.
DeStore
DeStore, a general store that has not yet opened in the center of San Francisco, is a DAO-operated store that has introduced a system in which those who own NFTs issued by the store vote on the store’s management policy. While attracting customers and forming a community through management by a DAO, the aim is to strengthen the connection with customers, creating a mechanism to attract customers to the store.
Although the number of cases utilizing DAOs is increasing in Japan and other countries around the world, it is still difficult to replace all organizational operations and business procedures with digital ones and complete them on the Internet. As with the implementation of blockchain, the industry is currently discussing which operations should be replaced digitally, and as shown in the case studies introduced above, more effective implementation methods are being sought in government and local governments.
To incorporate a DAO and make it a high-resolution business, the first step in implementation is to set up a hybrid format between the existing organization and the DAO and take advantage of the best parts of each format.
CTIA is promoting social implementation of DAO, blockchain, tokens, improvement of digital literacy necessary for the Web 3.0 era, and DX. If you are interested in business using DAO, please contact us via the inquiry form.
Writer:T.OGASAHARA