As digital transformation (DX) is widely introduced into the real world, “Web 3.0” has become the new buzzword. While Web 3.0 has been called a technology that will change the way society works and the next generation Internet, many people say it is just media speak and that they don’t really understand the concept. In this session, we will introduce “Web 3.0,” the changes and challenges it will bring to business, and how the future world will be shaped by it.
History of the Internet and how will the world will be changed by Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 is generally described as “a new decentralized network based on blockchain technology and other technologies.” But, to properly introduce Web 3.0, it is necessary to understand the existence of Web 2.0 and Web 1.0.
Today, the Internet has become so pervasive in our lives that it is difficult to imagine a world without it. However, when the Internet was first introduced in the 1990s, the flow of information on the Web was one-way. It was a bleak site with only company introductions and text. So, there were no opportunities for user interaction. However, Web 1.0 was also an era of democratization of information sharing in that individuals and companies were able to share information, which had always been the prerogative of newspapers and media.
In the 2000s, PCs became widely used in homes, and technologies developed improved PC performance and communication speeds. The birth of SNS, synonymous with Web 2.0, facilitated the sharing of images and videos between individuals, and the flow of information became real-time and two-directional. It has also been an era where the Big Five tech companies (Google, Apple, Facebook, Amazon, Microsoft) have reached the pinnacle of browsing capabilities; SNS; software; and hardware, with the result that information sharing has now spread to individuals all over the world.
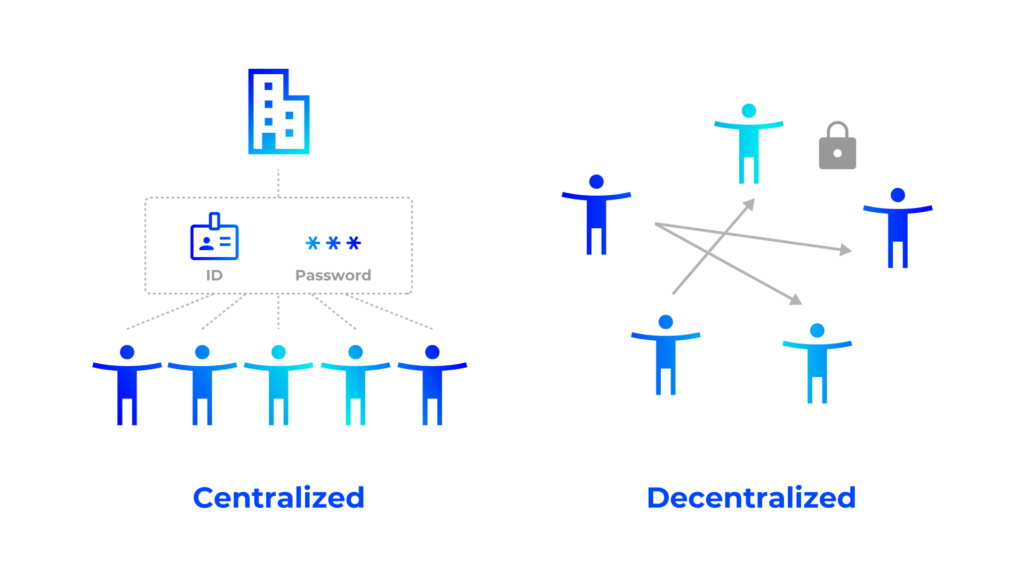
There are however many who view the concentration of information and data in the hands of specific companies as a problematic characteristic of Web 2.0. The oligopoly of information held by a few companies is a cause for concern over the leakage of personal information and the secondary use of privacy-related data.
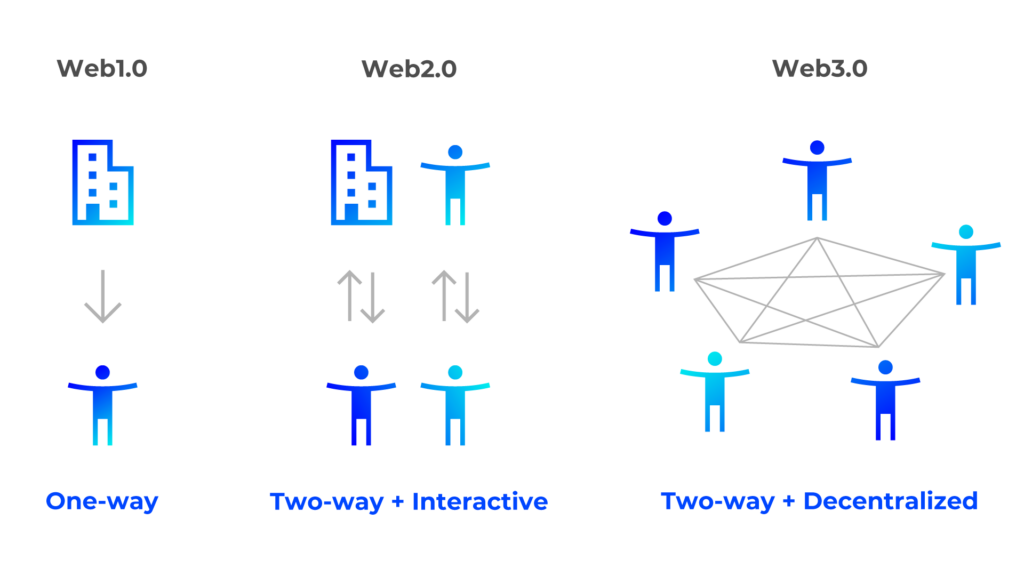
Web 3.0 is expected to solve the problems of Web 2.0. The concept of Web 3.0 is to make the sovereignty of information democratic by utilizing technology to decentralize and control the giant corporations that have monopolized the world’s information up to now.
Web 3.0 refers to building a more decentralized next-generation Internet by putting the control of data now centrally managed back in the hands of individuals by utilizing blockchain technology to manage and store their own information. In other words, Web 3.0 development is considered a shift toward democratization of information management.
Web 2.0 Issues
- Privacy and Centralization of Personal Information
Web 3.0 Benefits
- Decentralized・Distributed Model
- Ownership rights・Information rights in the hands of users
- Hierarchy- and platform-independent information management
Will Web 3.0 be a catalyst for market growth with the participation of governments and major foreign companies?
A succession of proposals for Web 3.0 by governments around the world are making headlines, and in March 2022, the U.S. was the first to take the lead on Web 3.0. President Biden issued a presidential decree encouraging technological innovation in digital assets, and the White House will now take the lead in considering policies related to digital assets such as crypto assets (virtual currency).
Following this trend, the UK Treasury also announced its commitment to the growth of the crypto asset sector in April this year. French President Macron mentioned the importance of Europe taking a leadership role in the area of Web 3.0. Although there has been no major movement within the Japanese government, members of the NFT Policy Review Project Team recommended to Prime Minister Kishida to make Web 3.0 a pillar of Japan’s growth strategy. The Policy Team has released a white paper urging the Japanese government to clarify its stance on formulating and promoting a national strategy for the Web 3.0 era.
Major international companies are also getting into the market. In May 2022 an internal team related to Web 3 and crypto assets was established by Google in the U.S. for services for developers who operate blockchain applications. In an internal email, Google announced the establishment of the team and stated this is a market with tremendous potential in response to the needs of users seeking support for Web 3.0 and crypto-asset related technologies.
These government proposals and the participation of major companies are evidence that Web 3.0 is a field of social significance, and the market is expected to grow in the future.
The Future Created by the Intersection of Web 3.0 and Metaverse
Similarly, Metaverse has become an equally big buzzword like Web3.0. Metaverse refers to a virtual space on the Internet based on 3D-CG technology, and has become a hot topic with games and commercial transactions as a starting point. If Web 3.0 is a transformation of how the Internet works, Metaverse has expanded the space of the Internet.
The Metaverse is also a developing market, but it has the potential to bring even greater disruptive innovation when it joins with the era of Web 3.0. Ultimately, the time when Web3.0 and Metaverse intersect will be the time when creators will be the champions. Existence of NFTs that give unique value in digital works that cannot be duplicated; dramatic improvement of 3D graphics from realization of large capacity communication by 5G; and refinement of machine learning by AI enables more creative data analysis at high-speed technological innovations—all of these enhance creators’ abilities to produce original digital works and characters.
For people and companies with IP (intellectual property) such as CG creators, character designers, and cartoonists, the world of Web3.0 and Metaverse might appear as a market known as a “blue ocean.”
Metaverse x Web3.0 has the potential to help many other industries and industries evolve one step further, but new ecosystems such as token economies and creator economies will be created to enable experiences that cannot be realized in reality with Metaverse. The future is just around the corner waiting to be born.
Challenges in Realizing a Digital Society through Web 3.0
Business competition is expected to intensify in order to take the lead in the digital continent of Web 3.0, but there are also many challenges to overcome.
Focusing on the crypto asset industry, there is a need to democratize blockchain technology as well as the tax and legal aspects surrounding the industry. Although there are an increasing number of cases of social trust both domestically and internationally, they are not widely known except among core fans and experts. Another reason for the lack of democratization is the small number of system integrators and other technology development personnel, as well as the limited investment and capital inflow into new industries and new economic areas.
From a broad perspective, it has been a long time since the present age was called the “VUCA” era, (Volatility, Uncertainty, Complexity, and Ambiguity.) It is also an important issue to prepare opportunities and environments to challenge a new industry without fear of failure, regardless of individuals or companies who might be in situations where it is difficult to predict the future.
It is not possible to transition to a new social form overnight, but it is possible now to reconcile the social form of Web 2.0 with the form advocated by Web 3.0. Medium- to long-term investments in experimental tests of the underlying technologies and exploration of business models are essential.
CTIA promotes the social implementation of blockchain and tokens, which are the foundation of Web 3, as well as the realization of the token economy and DX. We provide services that support blockchain consulting, overseas expansion, and industry-government-academia collaboration.
If you need more detailed business consulting in Web 3, please contact us through the inquiry form.

